The Hidden Gold Rush: How Singapore’s Scrapyards Are Transforming Urban Waste into Economic Opportunity
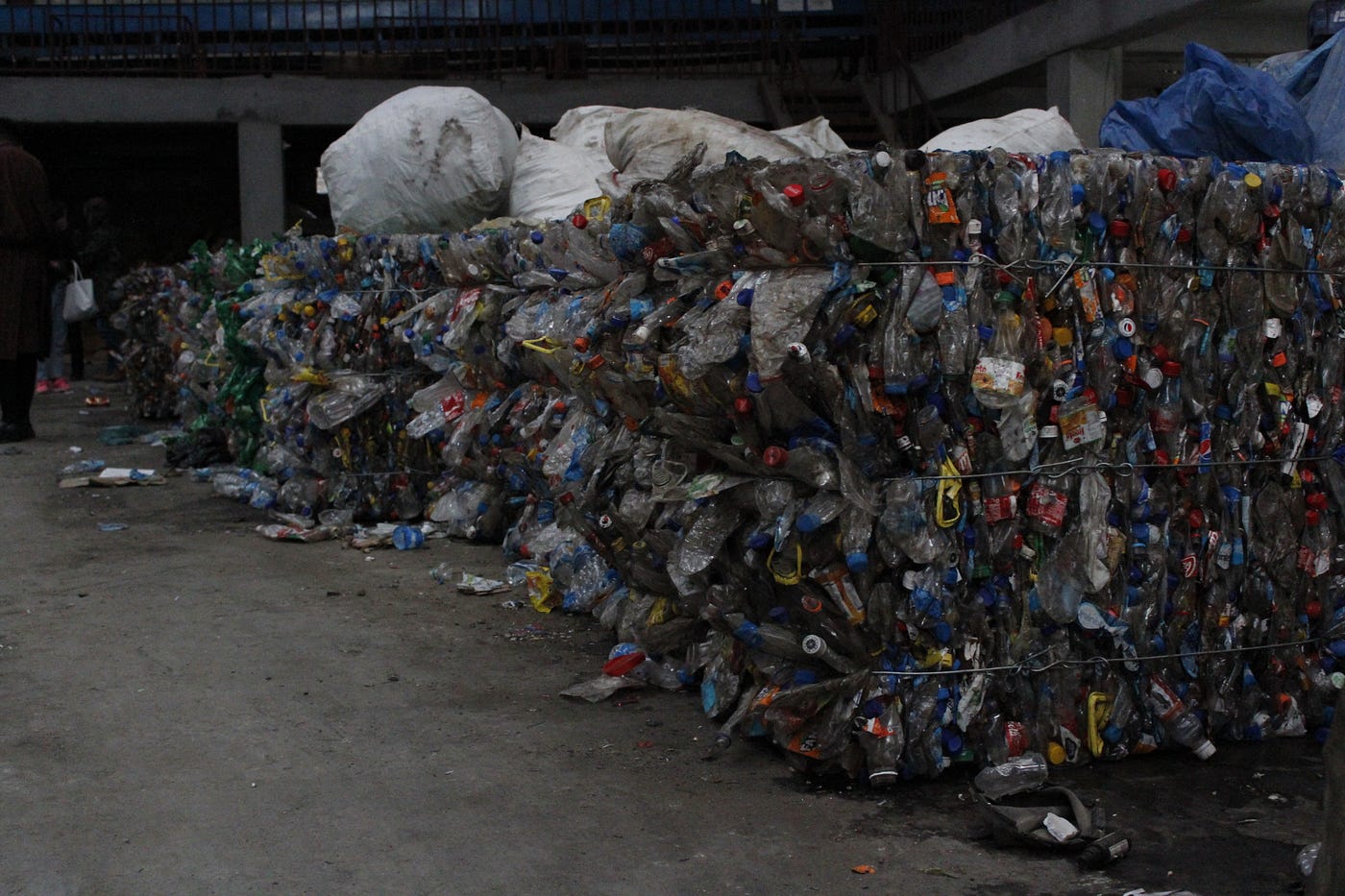
When searching for a scrapyard Singapore has to offer, most residents discover a thriving ecosystem that extends far beyond simple waste disposal. These industrial hubs represent a critical component of the city-state’s circular economy, where discarded materials find new life and contribute significantly to both environmental sustainability and economic growth.
The Economic Engine Behind Singapore’s Scrap Industry
Singapore’s strategic position as a global trading hub has naturally positioned it as a major player in the scrap metal trade. The island nation processes an impressive volume of recyclable materials annually, with the metalworking and recycling sectors contributing approximately S$2.8 billion to the economy each year. This substantial figure reflects not merely the volume of materials processed, but the sophisticated value-added services that local facilities provide.
The metal recycling industry has evolved considerably from its humble beginnings. What once comprised simple collection and basic sorting operations has transformed into technologically advanced facilities capable of processing everything from household appliances to industrial machinery. These operations employ cutting-edge separation technologies, ensuring maximum recovery rates and minimal environmental impact.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Metrics
Singapore’s commitment to environmental stewardship becomes particularly evident when examining the performance of its recycling infrastructure. The National Environment Agency reports that the country achieved a 52% overall recycling rate in 2022, with metal recycling contributing significantly to this figure. Specifically:
• Ferrous metals: 99% recycling rate
• Non-ferrous metals: 95% recycling rate
• Electronic waste: 60% recycling rate
• Automotive components: 85% recycling rate
These figures place Singapore amongst the world’s leading nations in material recovery, demonstrating how effective salvage yard Singapore operations contribute to broader environmental goals. The economic implications are equally compelling: every tonne of recycled steel saves approximately 1.5 tonnes of iron ore, 0.5 tonnes of coal, and reduces carbon emissions by 1.6 tonnes.
Technological Innovation in Material Processing
Modern auto scrapyard Singapore facilities bear little resemblance to the rudimentary operations of previous decades. Sophisticated magnetic separation systems, eddy current separators, and optical sorting technologies have revolutionised material recovery processes. These advances enable operators to extract valuable metals from complex assemblies with unprecedented precision.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has further enhanced operational efficiency. Advanced sorting algorithms can identify and separate materials with accuracy rates exceeding 95%, whilst predictive maintenance systems ensure optimal equipment performance. This technological sophistication has attracted international attention, with several multinational corporations establishing regional processing centres within Singapore’s industrial estates.
Regulatory Framework and Industry Standards
Singapore’s regulatory environment provides a robust foundation for responsible scrap processing operations. The Environmental Protection and Management Act sets stringent standards for vehicle dismantling activities, ensuring that hazardous materials are handled appropriately and that environmental contamination risks are minimised.
Licensed facilities must demonstrate compliance with:
• Proper handling protocols for hazardous substances
• Waste tracking systems ensure full material accountability
• Environmental monitoring programmes
• Worker safety standards exceeding international benchmarks
• Financial guarantees covering potential environmental liabilities
This comprehensive regulatory framework has fostered industry professionalism whilst ensuring that operations maintain the highest environmental and safety standards.
Economic Opportunities and Market Dynamics
The metal scrap dealers Singapore market demonstrate remarkable resilience and growth potential. Global commodity prices significantly influence local operations, with fluctuations in steel, aluminium, and copper prices directly impacting processing volumes and profitability. However, Singapore’s diversified industrial base provides stability through consistent domestic supply streams.
Recent market analysis indicates that the local scrap metal trade generates approximately S$450 million annually in direct revenue, supporting over 3,500 jobs across collection, processing, and distribution activities. These figures exclude the substantial indirect economic benefits generated through reduced raw material imports and decreased landfill requirements.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite impressive performance metrics, Singapore’s scrap industry faces several significant challenges. Limited land availability constrains facility expansion opportunities, whilst increasing labour costs pressure operational margins. Additionally, evolving international trade policies and environmental regulations require continuous adaptation and investment.
However, emerging opportunities present compelling growth prospects. The transition towards electric vehicles will generate substantial volumes of lithium-ion batteries requiring specialised processing capabilities. Similarly, Singapore’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 will drive increased demand for recycling centre Singapore services across all sectors.
Government initiatives supporting circular economy principles provide additional momentum. The Resource Efficiency Grant for Energy and Water supports facility upgrades, whilst the Industrial Transformation Map for Environmental Services identifies specific growth areas and development priorities.
The Path Forward
Singapore’s scrap processing industry exemplifies how small nations can achieve an outsized impact through strategic positioning and technological innovation. The sector’s evolution from basic material recovery to sophisticated value-added processing demonstrates the potential for sustainable industrial development within urban environments.
As global awareness of environmental issues intensifies and resource scarcity becomes increasingly pressing, Singapore’s expertise in efficient material recovery will become ever more valuable. The integration of advanced technologies, comprehensive regulatory frameworks, and strong economic incentives has created a model that other nations increasingly seek to emulate.
The future remains bright for this essential industry, with continued growth expected as Singapore maintains its position as a leading destination for businesses seeking reliable scrapyard Singapore services.